Researchers from the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Polish Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with teams from Sapienza University of Rome, and Technical University of Denmark, have developed a new experimental cellular model to study mitochondrial potassium channels—key regulators of cellular energy metabolism and protection against stress.
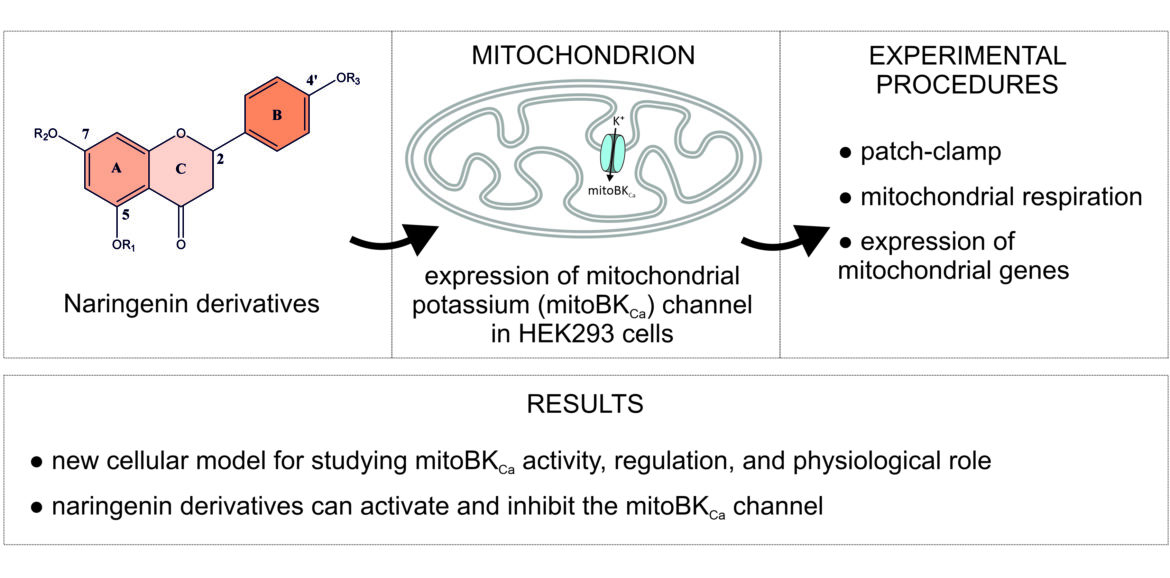
The study, published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports, describes the creation of a HEK293 cell line expressing the VEDEC isoform of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (BKCa), which forms the mitochondrial BKCa (mitoBKCa) channel. Using this model, the team demonstrated that the presence of this channel profoundly alters mitochondrial respiration and gene expression related to energy metabolism.
Importantly, the researchers used this system to test new derivatives of the natural flavonoid naringenin, revealing that subtle chemical modifications can either activate or inhibit the mitoBKCa channel. Since activation of these channels is known to protect tissues from ischemia/reperfusion injury, the findings open new perspectives for designing mitochondria-targeted therapeutics based on flavonoid scaffolds.
“Our new model provides a powerful tool to study mitochondrial potassium channels with defined molecular composition,” says Dr. Bogusz Kulawiak, the corresponding author. “It will enable screening of new compounds that could support mitochondrial function or modulate cellular metabolism in disease contexts.”
The research highlights how naturally occurring compounds such as naringenin—found in citrus fruits—can influence mitochondrial physiology, suggesting new directions for pharmacological development and metabolic research.
Publication:
A. Sęk, S. Cammarone, R.P. Kampa, K. Pytlak, B. Kalenik, J. Lewandowska, F. Ghirga, I. Romeo, O. Atrooz, P. Bednarczyk, A. Szewczyk, B. Botta, D. Quaglio, B. Kulawiak.
“Regulation of mitochondrial potassium BKCa channel by naringenin derivatives: application of a new cellular model.”
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports (2025), 15:100304.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmcr.2025.100304